Inorganic insulating materials for house construction
Problem
In the future, mankind will have only very limited access to fossil fuels. We are already feeling the consequences in our everyday lives. The Gernman "Energieeinsparverordnung", for example, prescribes to citizens the extent to which their own house must be insulated. Often, problematic insulating materials such as Styropor, which is derived from petroleum, are used because they are cheap. There are two problems associated with Styrofoam: It is combustible and acts as a vapor barrier, which promotes mold growth in the house.
Solution
An aqueous silicate solution is foamed with the aid of foaming agents without the application of external heat, similar to a polyurethane foam. By adding a hardener, the foam solidifies within minutes. The foam stone formed is purely inorganic and non-flammable. The foaming process can be carried out in a mold. The product is non-combustible and permeable to water vapor.
Details
Thermal insulating capacity of foam blocks
The thermal insulating capacity of a foam block depends on its density and pore structure. The lower the density, the better the material insulates. However, as the density decreases, so does the stability of the material. It is therefore important to create the smallest possible bubble structures in the brick, because in small bubbles the convection of air is hindered. This is the only way to create an optimum thermal insulation effect.
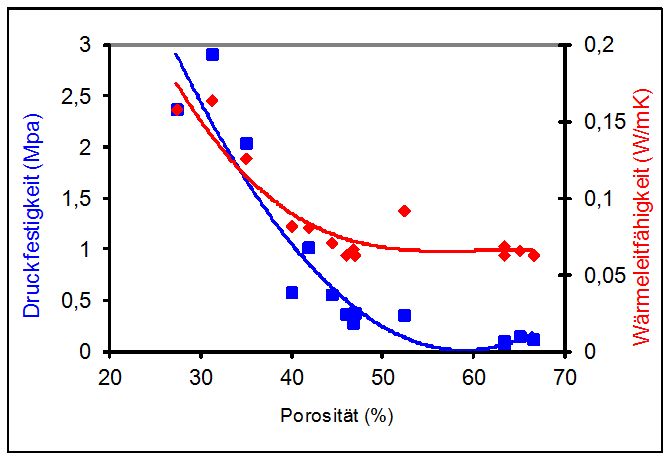
Relationship between porosity and thermal conductivity
The following graph shows the relationship between density and thermal conductivity for selected specimens. It can be seen that bodies with high density (lower porosity) have better thermal conductivity than bodies with low density (higher porosity).
The performance of the Institute NaSiO

The NaSiO-employees able to produce incombustible foam stones with density from 0.07 - 2.5 g/cm3. The pore size is adjustable in a wide range from a few micrometers to millimeters.
These foam bricks exhibit thermal conductivities between 45 and 200 mW/(m*K) and are excellent for interior house insulation. The bricks are temperature and light stable. They are made of non-toxic materials. Their basic alkaline structure prevents algae and mold growth.
The NaSiO-employees are working on similar foam bricks for external insulation of buildings.
Their insulating bricks can also be used in fire protection and are ideal for protecting escape routes, elevators and electrical equipment.
On request, they produce foam blocks for insulation purposes with specific requirements.
![[Translate to English:] Zierprofil [Translate to English:] Zierprofil](/fileadmin/Sonstige_Unterseiten/INaSiO/images/Zierprofil.png)